Understanding Encryption, SSL, and TLS
Encryption is the foundation of secure digital communication, converting readable data into unreadable ciphertext to prevent unauthorized access. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are encryption-based protocols that protect data transmitted over networks, such as websites, emails, and cloud services. By ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authentication, SSL/TLS enables secure connections between clients and servers, making them essential for modern network security. Tools like NEOX PacketShark allow organizations to monitor SSL/TLS traffic safely, ensuring visibility and performance without compromising encrypted data.
What Is Ciphertext?
When data is encrypted, it is transformed from its original readable form, called plaintext, into an unreadable format known as ciphertext. Ciphertext appears as a random string of characters and cannot be understood without the correct decryption key.
Example:
- Plaintext: MyPassword123
- Ciphertext (AES encryption): 8f3d2a9b1c4e6f0a9d7b…
This process ensures that even if intercepted, the data cannot be read by unauthorized parties. The conversion between plaintext and ciphertext is what makes encryption secure.
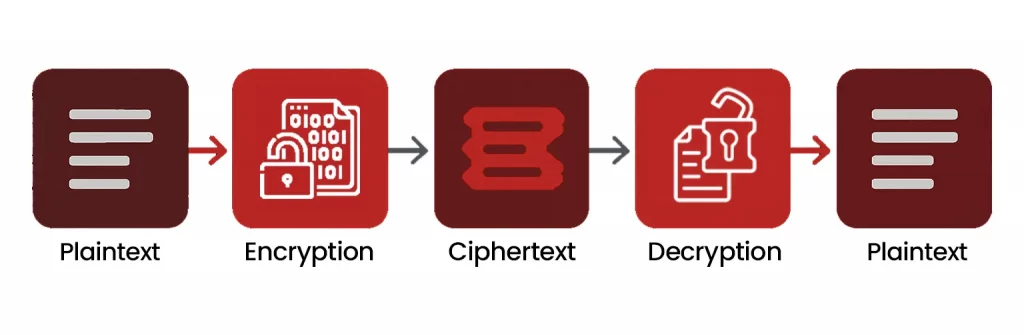
Diagram 1 : Ciphertext Flow
What Is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of converting readable data (plaintext) into unreadable code (ciphertext) to prevent unauthorized access. Only someone with the correct decryption key can revert it to its original form.
Encryption protects data in transit and at rest, from emails and web traffic to files stored on servers. It’s the backbone of secure communications and network protection.

Diagram 2 : Encryption Flow
How Encryption Works
Encryption relies on algorithms and keys:
- Encryption Algorithm: Defines how data is transformed into ciphertext.
- Key: Determines the exact output of the encryption process.
Types of encryption:
- Symmetric Encryption: Same key used for both encryption and decryption (e.g., AES). Fast and efficient.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Uses a public key to encrypt and a private key to decrypt (e.g., RSA). Offers stronger security for data exchange.
Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the correct key.
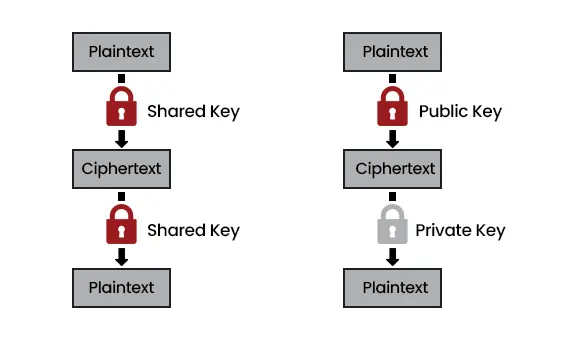
Diagram 3 : Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption
What Are SSL and TLS Protocols?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are protocols that encrypt data transmitted over networks. They protect sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, and internal communications.
TLS is the modern, more secure successor to SSL. Both protocols provide:
- Encryption: Secures data in transit
- Authentication: Confirms the identity of servers
- Integrity: Ensures data isn’t tampered with during transmission
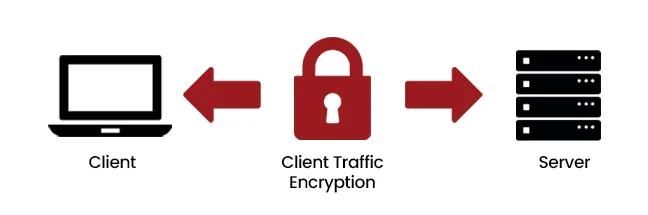
Diagram 4 : HTTPS Traffic Encryption Between Client & Server
SSL/TLS Handshake Process
- Client requests a secure session.
- Server responds with a digital certificate proving its identity.
- Both sides agree on encryption algorithms and session keys.
- Encrypted communication begins using the session key.
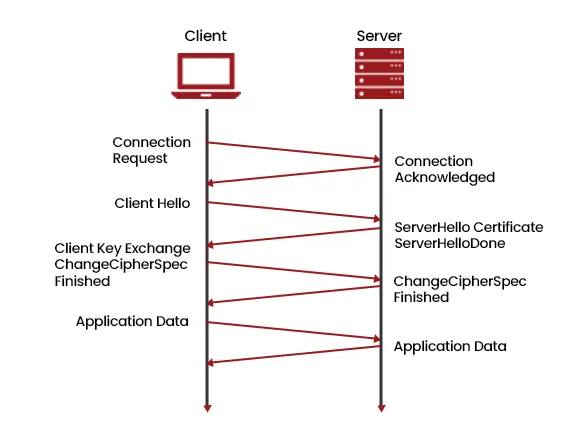
Diagram 5 : SSL/TLS Handshake
Encryption in Network Monitoring
Encrypted traffic poses challenges for monitoring, troubleshooting, and threat detection. Products like NEOX PacketShark make SSL/TLS traffic analysis easier without compromising security. PacketShark allows teams to capture, inspect, and monitor encrypted traffic safely for:
- Performance optimization
- Threat detection
- Compliance reporting (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.)
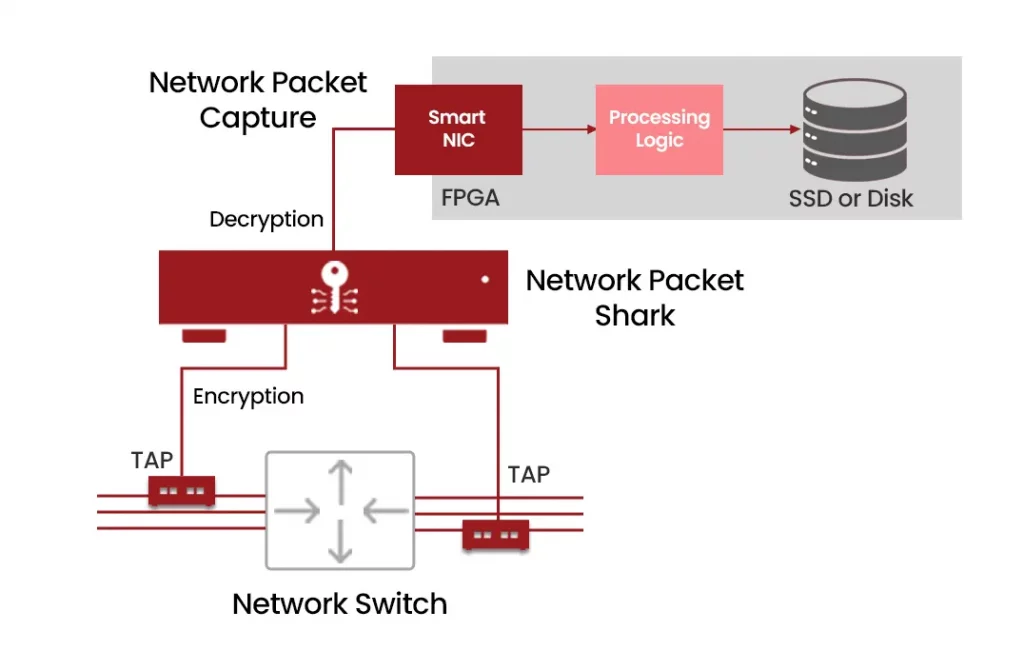
Diagram 6 : PacketShark capturing SSL/TLS traffic
Why Encryption Matters
Encryption is critical in modern network security:
- Prevents eavesdropping and unauthorized access
- Maintains data integrity and authenticity
- Ensures compliance with regulatory standards
- Essential in VPNs, cloud networks, and enterprise systems
SSL/TLS Traffic Analysis with PacketShark
NEOX PacketShark is designed for encrypted network environments:
- Captures SSL/TLS traffic in real-time
- Provides detailed insights without fully decrypting sensitive data
- Helps detect anomalies, optimize traffic flow, and maintain compliance
“With PacketShark, network teams can securely monitor encrypted traffic while maintaining visibility and control over their network.”

Diagram 7 : PacketShark SSL/TLS
FAQs
What is the difference between SSL and TLS?
TLS is the updated, more secure version of SSL, offering stronger encryption and authentication.
Can SSL/TLS traffic be analyzed safely?
Yes, tools like PacketShark allow monitoring encrypted traffic without exposing sensitive data.
Why is encryption important in network security?
It prevents unauthorized access, ensures data integrity, and protects sensitive communications.
How do digital certificates work?
Certificates verify server identity and enable encrypted connections between clients and servers.
Can encrypted packets be monitored without decryption?
Yes, PacketShark enables encrypted packet analysis for visibility and performance monitoring.

